This paper describes the design and the performance of simultaneous, multifrequency impedance measurement system for four inductive-loop (IL) sensors which have been developed for vehicle parameters measurement based on vehicle magnetic profile (VMP) analysis. Simultaneous impedance measurement on several excitation frequencies increases the VMP measurement reliability because typical electromagnetic interferences (EMI) are narrowband, and should not simultaneously affect, in the same way, all measurement bands that are spread in the frequency, i.e., it is expected that at least one measurement band is disturbance-free. The system consists of two standard and two slim IL sensors, specially designed and installed, the analogue front-end, and an industrial computer with digital-to-analogue and analogue-to-digital converters accessed via field-programmable gate array (FPGA). The impedance of the IL sensors is obtained by vector measurement of voltages from auto-balancing bridge (ABB) front-end. Complex voltages are demodulated from excitation frequencies with FIR filters designed with the flat-top windows. The system is capable of delivering VMPs in real-time mode, and also storing voltages for off-line postprocessing and analysis. Field distributions and sensitivities of slim and standard IL sensors are also discussed. Field test confirmed assumed increased reliability of VMP measurement for proposed simultaneous multifrequency operational mode.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s20174933
Publikacja
Abstract: The paper presents a low-cost electronics system for impedance measurement of an inductive-loop sensor as well as small, rapid changes in impedance components. The idea of the system is based on the adaptation of a vector voltmeter instead of the Maxwell-Wien bridge balance indicator and supporting the system with a microcontroller. The proposed procedures, based on the complex voltage of bridge unbalance, allow to calculate the resistance that can balance the bridge in a short time. This, in turn, allows to measure the sensor impedance components, identically, as in the case of a well-known balanced bridge method. However, what is original in this work, is that measurements can be taken in a state of bridge imbalance and with high relative accuracy to small changes in sensor impedance.
Keywords: Maxwell-Wien, Bridge, Vector voltmeter, Impedance, Inductive-loop, Vehicle axle, Magnetic signature
https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MEASUREMENT.2018.02.038
Publikacja
Abstract: The possibility of using the inductive loop sensor as an efficient axle detector of vehicles is presented in the hereby paper. The fundamental condition for using such sensors is the proper selection of its geometrical dimensions. The original conditioning system was applied for cooperating with the sensor. At this system’s output two signals (magnetic profiles) proportional the changes in its impedance components are obtained. Identification results of the function parameters allowing the optimal fusion of the conditioner output signals for various vehicle classes, as well as the axle detection algorithm, were also presented. The applying inductive sensors good point is the possibility of detecting lifted axles in vehicles, which is impossible when currently widespread load sensors are applied.
Published in: 2016 21st International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR)
DOI: 10.1109/MMAR.2016.7575082
Publikacja
ITS, R-profile, vehicle axle detection, X-profile
This paper presents the state of currently used technological solutions employed in research regarding the use of inductive loop sensor (IL) for vehicle axle detection. Inductive loop sensors are less expensive and more durable than other sensors available on the market. What is more, they are the only type of sensor that enables lifted axle detection. System with such sensors may be used for measurement of speed, number, distance and arrangement of vehicle axles. Available know-how of sensor constructions and signal conditioners are also presented, in particular: LC-generators, microloops, “blade” sensors, AC-bridge base system, and a new system based on changes in the IL impedance components. The new solution of the system cooperating with narrow IL is the original part of the paper. This system allows independent measurement of the changes in the IL impedance components. Latest research has shown that the efficiency of the vehicle axle detection of this system, ranges from 98-100 %, and 71.8 % for vehicles traveling with a lifted axle. It should be stressed that other sensors do not allow the detection lifted axles at all. This means that the inductive loop sensors can successfully replace the less durable and more expensive traditional vehicle load axle detectors.
- DOI: 10.1109/MMAR.2015.7283972
-
Publikacja
ITS, R-profile, X-profile
Sposób pomiaru składowych impedancji czujnika indukcyjnego i układ pomiarowy składowych impedancji czujnika indukcyjnego. Patent
Publikacja
Aktualnie stosowane rozwiązania, umożliwiające detekcję osi pojazdów samochodowych, bazują na mechanicznych czujnikach nacisku, po których przejeżdża pojazd. Powszechnie stosowane są czujniki piezoelektryczne, lub o wiele droższe, kwarcowe, umożliwiające poza detekcją osi, ważenie pojazdów w ruchu (WIM). Tam, gdzie nie jest wymagana informacja o masie pojazdu, a wymagana jest klasyfikacja pojazdów ze względu na liczbę i ułożenie osi, drogie systemy WIM nie są konieczne. Nie zawsze sprawdzają się w stu procentach, ponieważ samochody ciężarowe mogą podnosić przynajmniej jedną oś. Systemy bazujące na pętli indukcyjnej, dzięki innej zasadzie działania, pozwalają na detekcję również podniesionych osi, przez co możliwa jest poprawna klasyfikacja pojazdów ciężarowych. Pętle indukcyjne charakteryzują się bardzo dużą trwałością oraz prostą budową. Czas ich eksploatacji wielokrotnie przekracza czas eksploatacji stosowanych detektorów. Pętle indukcyjne do detekcji osi pojazdów wymagają stosowania bardzo czułych układów kondycjonowania nowej generacji.
Z. Marszałek, Detekcja osi pojazdów z użyciem pętli indukcyjnej, Zeszyty Naukowe Wydziału Elektrotechniki i Automatyki Politechniki Gdańskiej, 2013 nr 34, s. 43–47.
Publikacja
czujnik indukcyjny pętlowy, ITS, profil R, Profil X
W artykule przedstawiono praktyczną realizację prototypu oraz wyniki badań eksperymentalnych zaproponowanego przez autorów pojemnościowego detektora wilgotności skóry. Omówiono budowę detektora, przyjęty model skóry oraz przedstawiono sposób realizacji detektora i badań laboratoryjnych jego właściwości metrologicznych. Przedstawiono wyniki pomiarów pokazujące zależność pojemności detektora od wilgotności względnej materiału higroskopijnego. Podczas badań eksperymentalnych prototypu detektora stwierdzono duży wpływ siły docisku detektora do powierzchni próbki na wartość pojemności.
W. Gawędzki, Z. Marszałek, Praktyczna realizacja oraz badania eksperymentalne pojemnościowego detektora wilgotności skóry, Pomiary, Automatyka, Kontrola, 2013 vol. 59 nr 3 s. 247–249.
Publikacja
detektor pojemnościowy wilgotności
W artykule przedstawiono wyniki badań symulacyjnych zaproponowanego przez autorów pojemnościowego detektora wilgotności skóry. Omówiono budowę detektora, przyjęty model skóry oraz przedstawiono sposób modelowania ich właściwości dla potrzeb obliczeń numerycznych metodą elementów skończonych. Przedstawiono wyniki symulacji pokazujące zależność pojemności detektora od przenikalności elektrycznej skóry. Proponowany detektor wilgotności może znaleźć zastosowanie podczas tzw. treningu biofeedback, do obserwacji reakcji wilgotności skóry na zmiany chorobowe organizmu, do sprawdzania działania środków kosmetycznych, leków itp.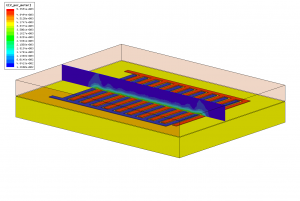 W. Gawędzki, Z. Marszałek, Badania symulacyjne pojemnościowego detektora wilgotności skóry, Pomiary, Automatyka, Kontrola, 2012 vol. 58 nr 4, s. 358–360.
W. Gawędzki, Z. Marszałek, Badania symulacyjne pojemnościowego detektora wilgotności skóry, Pomiary, Automatyka, Kontrola, 2012 vol. 58 nr 4, s. 358–360.
Publikacja
detektor pojemnościowy wilgotności, wilgotność skóry
W pracy przedstawiono trójwymiarowy model polowy czujnika indukcyjnego pętlowego. Do uzyskania rozkładu pola magnetycznego wykorzystano aplikację Maxwell 3D. Omówiono przygotowanie modelu oraz przedstawiono wybrany rozkład amplitud indukcji sinusoidalnej generowanej przez czujnik w obecności obiektu metalowego. Obliczone z rozkładu pola parametry impedancji czujnika zestawiono ze zmierzonymi parametrami impedancji rzeczywistego czujnika i przeprowadzono weryfikację modelu poprzez porównanie kształtów sygnałów uzyskanych z pomiarów z sygnałami uzyskanymi z modelu polowego.
Z. Marszałek, Model polowy czujnika indukcyjnego pętlowego, Materiały XVIII Sympozjum Modelowanie i Symulacja Systemów Pomiarowych, 2011, Krynica, s. 19 – 26. Read more…
Publikacja
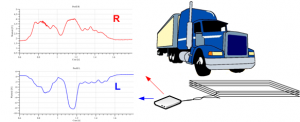
profil L, profil R
W pracy przedstawiono model systemu do automatycznej rejestracji profili magnetycznych pojazdów. System posiada możliwość zdalnego nadzoru oraz zmiany ustawień systemu poprzez sieć Internet. Przedstawiono również otwarte technologie internetowe w praktycznym zastosowaniu. Omówiono budowę systemu, warstwę sprzętową, zasadę działania oraz oprogramowanie rejestrujące. Przedstawiono również rozwiązania niektórych problemów związanych ze zdalnym dostępem zarówno do systemu, jak i do gromadzonych przez niego danych. Pokazano zastosowanie i korzyści wynikające z użytych w nim otwartych technologii internetowych umożliwiających zdalny, tunelowany dostęp do systemu za pomocą modemu GSM z dostępem do Internetu.
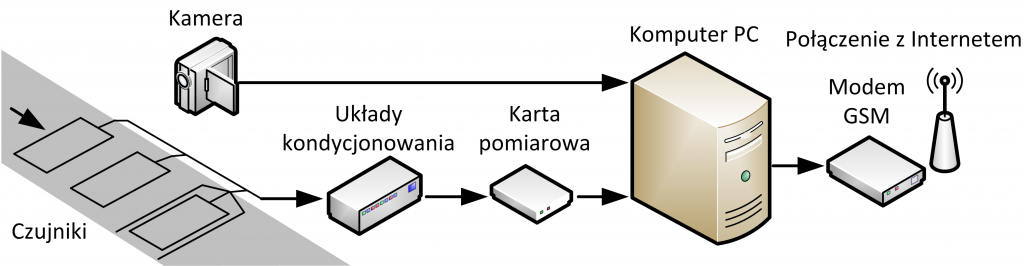
Z. Marszałek, M. Mielczarek, Model systemu oraz otwarte technologie internetowe w zdalnym systemie do automatycznej rejestracji profili magnetycznych pojazdów, Materiały XVIII Sympozjum Modelowanie i Symulacja Systemów Pomiarowych, 2011, Krynica, s. 175 – 180.
Publikacja
pomiar parametrów ruchu pojazdów, profil L, profil R, traffic-1


